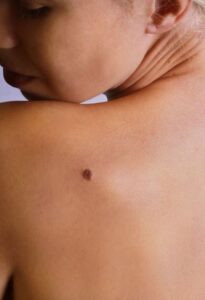
A nevus, or mole, is an area of growth on the skin. Some moles are present at birth, while others develop over the course of your lifetime. Many of the moles that develop during adulthood are related to sun exposure and effects on melanin production.
While mostly thought of as brown, moles can come in a variety of colors, including red, pink, and flesh-colored. Some may also have hairs that grow from them.
Most moles are benign, but it’s still important to keep an eye on them for any changes that could indicate cancer growth.
Types of Moles
There are three main types of moles:
Congenital Moles
Congenital moles are present at birth, which affect about 1 out of every 100 babies, but most congenital moles don’t become cancerous.
Acquired Moles
Acquired moles are those that you develop later in life. Most of these are brown and appear due to sun damage. They’re also round without any significant changes as you age. These types of moles can also darken with age, but not necessarily turn into melanoma.
Atypical Moles
Unlike congenital and acquired nevi, atypical moles are at a greater risk of becoming cancerous.
Unlike congenital and acquired moles, atypical moles are slightly larger and have irregular-shaped borders.
When to have a mole checked by a doctor?
Dermatologists recommend an annual skin checkup. At this time, they’ll look at any existing moles for changes, as well as any potential cancerous growth.
If you see any concerning changes to your skin in between your annual checkups, you should make an appointment.
Some of the changes that warrant a doctor’s check include:
- any new, rapidly growing moles
- a mole that suddenly changes in shape or size
- moles that are extremely itchy
- any mole that bleeds on its own without injury or looks infected
- You may also be at a higher risk of cancerous skin spots if you have more than 50 acquired moles, according to the AAD.
What to look for?
When it comes to looking out for the signs of skin cancer, the AAD reminds us to remember the ABCDEs of melanoma:
- Asymmetry
- Border: irregular and sometimes poorly defined
- Color: can vary in same mole
- Diameter: usually 6mm or larger
- Evolving