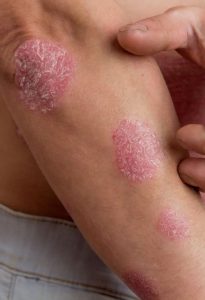
Eczema treatment in Dwarka Sector 8 Delhi
Eczema is a condition where in patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, cracked, and rough. Some types can also cause blisters.
The specific cause of eczema remains unknown, but it is often caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Small children whose parents have an atopic disease; the risk of having eczema in them is higher.
Symptoms in infants
The following atopic dermatitis symptoms are common in infants under the age of 2:
- Rashes on the scalp and cheeks
- Rashes that bubble up before leaking fluid
- Rashes that can cause extreme itchiness, which may interfere with sleeping
Symptoms in children
The following atopic dermatitis symptoms are common in children age 2 and above:
- Rashes that appear behind the creases of elbows or knees
- Rashes that appear on the neck, wrists, ankles, and the crease between the buttocks and legs
- Bumpy rashes
- Rashes that can become lighter or darker
- Skin thickening, also known as lichenification, which can then develop into a permanent itch
Symptoms in adults
The following atopic dermatitis symptoms are common in adults:
- Rashes that are more scaly than those occurring in children
- Rashes that commonly appear in the creases of the elbows or knees or the nape of the neck
- Rashes that cover much of the body
- Very dry skin on the affected areas
- Rashes that are permanently itchy
- Skin infections
Certain substances or conditions called trigger factors can cause eczema to flare-up:
- Irritants such as soaps and detergents, wool, skin infections, dry skin, low humidity, heat, sweating or emotional stress.
- Allergens such as dust mites, pollen, moulds, or foods.
- Food items such as soy products, eggs, nuts, dairy products can cause eczema flare-ups.
- Environmental factors, pollen grains, dust, mould, mites, and animal fur
- Certain fungi, microbes, and staphylococcus bacteria.
- Stress, hormonal changes, and change in seasons (hot and cold temperature) are responsible for causing eczema.